概述
spring boot transaction我们平时用着非常简单,只需要在service方法上声明@Transactional就可以了。但是要知道,简单的背后是不简单,只是很多东西spring框架帮我们做好了。如果想进阶,想进步,想弄懂,想学习,需要接近它,了解它,弄懂它,最好的方法莫过于debug它的源码了。
笔者把spring boot transaction的整个过程分为两个阶段
- 带有@Transactional方法的service类生成代理类的阶段
- 访问service类的@Transactional方法实现事务的阶段
本文说下第一阶段,用过spring的人差不多都是知道,spring 事务的实现是通过aop的方式。所以本系列的前提是基于注解的aop实现解析你要知道些,这部分请参考:spring boot aop过程解析之阶段一 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator加载和初始化, AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是aop动态代理的起始点和入口处,所有的beanClass经过通过他的实例化前置方法和所有的bean Object经过他的初始化后置方法时都会判断是否生成代理类。笔者假定你了解了这部分。
本文用到的代码项目:springboot_mybatis
技术栈
1 | spring boot 1.5.10 |
用例代码
1 | @RestController |
以上代码模拟了实际开发中mvc层级调用关系,事务在service层。我们以此代码为例阐述spring事务相关知识点
带着问题学习
带着问题学习往往起到更好的效果
问题:1
2
3
41. service类只要有方法加了@Transactional注解就会生成代理类吗,此处的方法有条件吗
2. spring boot 涉及transaction事务的xxxAutoConfiguration都有哪些
3. spring boot 默认生成代理的方式是cglib还是jdk
4. 什么样的方法可以生成代理方法
下面开始和笔者一起走入spring aop生成代理类的小溪,从本文开头处我们知道,生成代理类的入口是AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator(使用父类的方法)实例化前置方法和初始化后置方法(如果此处不太了解,请参考:spring boot aop过程解析之阶段一 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator加载和初始化)。我们直接从此处展开
生成代理类条件判断
我们看下前后置方法的代码。同样,因为这里在spring boot aop过程解析之阶段一 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator加载和初始化)已经阐述过。所以这里我们只关注和spring transaction有关的地方1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
······
// shouldSkip方法是重点,判断是否应该为beanClass生成代理类
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) { // (1)
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
// Create proxy here if we have a custom TargetSource
if (beanName != null) {
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource); // (2)
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
}
return null;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
······
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { // (1)
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); // (2)
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); // (3)
return proxy;
}
return bean;
}
这里我们只列出了关键代码。可以看到两个方法在判断是否生成代理类时都用到了(1)处shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)方法。此方法主要逻辑为获取Advisor类型的beans,如果获取到判断是否为Aspect切面相关的逻辑,否则直接走super即AbstractAutoProxyCreator.shouldSkip逻辑,这个方法默认是false。此处的重点是获取Advisor类型的beans,获取的地方是BeanFactory容器。
调用栈为:
具体代码为:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper class 这个类是专门从BeanFactory获取Advisor的
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() {
// Determine list of advisor bean names, if not cached already.
String[] advisorNames = null;
synchronized (this) {
advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames; // 额外的问题,这句应该放到synchronized外更好吧?
if (advisorNames == null) {
advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false);
this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames;
}
}
List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
for (String name : advisorNames) {
if (isEligibleBean(name)) {
try {
advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class));
}catch (BeanCreationException ex) {throw ex;}
}
}
return advisors;
}
上面方法代码使用BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors()获取Advisor类型className,同时这里使用了缓存方便以后使用。然后通过beanFactory.getBean(name,Class)方法获取bean实例并返回。实际debug时,我们获取的advisorName是org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor,为什么是它呢,我们先看看这个东西是啥,在哪用了,代码如下1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37public abstract class TransactionManagementConfigUtils {
/**
* The bean name of the internally managed transaction advisor (used when mode == PROXY).
*/
public static final String TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME = "org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor";
}
@Configuration
public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor() {
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor());
advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
return advisor;
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor() {
TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
if (this.txManager != null) {
interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
}
return interceptor;
}
}
可以看到ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.transactionAdvisor()方法的@Bean的name属性使用了org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor作为value,这里我们需要说下带有@Configuration和@Bean的class解析过程,带有@Bean的方法会被ConfigurationClassParser解析为一个BeanDefinition,然后将这个BeanDefinition方法DefaultListableBeanFactory.beanDefinitionMap属性中key:org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor”,value:BeanDefinition; 同时将org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor放入DefaultListableBeanFactory.beanDefinitionNames中。所以上面的BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans()能通过BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors()方法取到org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor,而beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class)方法会从DefaultListableBeanFactory.beanDefinitionMap获取到key对应的value,即BeanDefinition对象,进而解析这个BeanDefinition,解析就是将BeanDefinition实例化成Bean Instance,具体体现就是生成BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor实例,解析的过程用过了动态代理,具体参见:TODO
生成的BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor实例为作为value, org.springframework.transaction.config.internalTransactionAdvisor作为key放入DefaultListableBeanFactory.singletonObjects。生成BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor实例的过程中,由于用到了transactionAttributeSource和transactionInterceptor。所以,这两个实例也会以同样的方式生成。
到这,和spring transaction事务相关的advisor实例就找到了,即BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor实例,他包含transactionAttributeSource、切入点:TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut和切面:transactionInterceptor拦截器。(1)处代码shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)方法到这就走完了,这个过程中advisor被找到放到beanFactory中,对应的advisorName放入缓存中,后面的每个beanClass和bean经过前后置方法时不必再走一遍寻找Advisor的逻辑,看见缓存中有就直接使用。
(1)处返回false,程序往下走(2)处代码getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean,看名字我们能知道大概:获取Advisor,看下这里。又我们前面定义了UserServiceImpl类,我们想通过这个类来了解spring transaction事务,又因为每个beanClass和bean都会走AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator前后置方法。为了能快读定位到我们定义的UserServiceImpl,所以我们在前后置方法的shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)一行打个带条件的断点(breakpoint),如下图
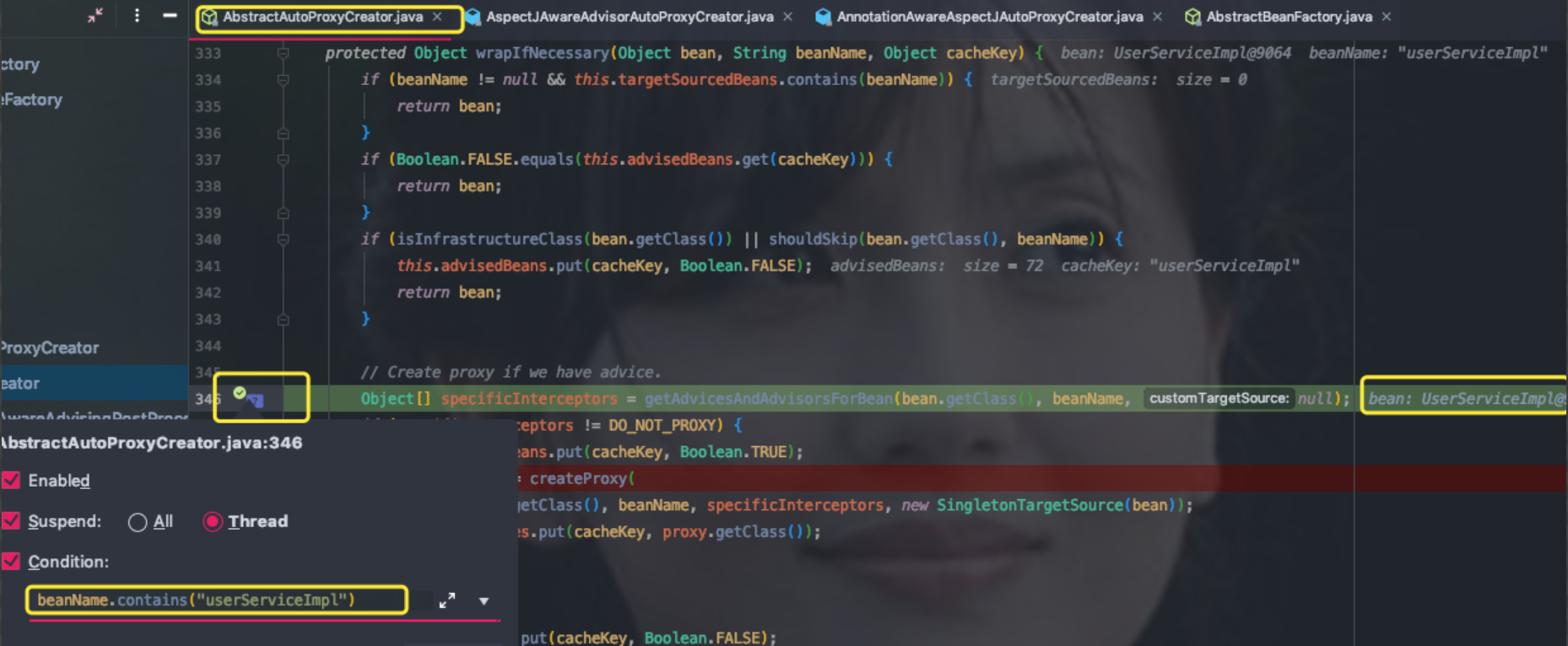
这样只有符合条件才会停在断点上。现在我们可以一步一步debug来观察UserServiceImpl怎样关联spring transaction事务的。断点进入getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法。getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法做两件事:获取Advisor和判断Advisor是否能应用到目标beanClass(UserServiceImpl)。看代码1
2
3
4
5
6protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); // 获取Advisor
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); // 判断Advisor是否能应用到目标beanClass
// eligibleAdvisors不为空才会生成代理类
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
获取到的Advisor即是是我们刚详细阐述的BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor。下面看下判断Advisor是否能应用到目标beanClass逻辑。我们知道BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor有个pointcut属性:TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut,实例化BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor时,TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut也跟着实例化了。是否能应用到目标beanClass的逻辑就在这里,看代码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, false)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
AopUtils class
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {
// MethodMatcher即为TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
classes.add(targetClass);
// 遍历目标类的方法,依次进行匹配,只要有一个匹配上,返回true,表示可以应用
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null &&
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) ||
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut class
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null); // 能获取TransactionAttribute就表示匹配
}
AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource class
public TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
······ // 前后是有缓存的
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
return txAttr;
}
AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource class
protected TransactionAttribute computeTransactionAttribute(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
// AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource.publicMethodsOnly的值为true且目标方法的修饰符是public才有可能,否则直接返回null
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
// 在目标方法上获取TransactionAttribute
TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod);
if (txAttr != null) {
return txAttr;
}
// 如果目标方法上没有,看看在目标方法的类上获取TransactionAttribute
txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass());
if (txAttr != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return txAttr;
}
// 都没有获取到,返回null,表示没有获取到TransactionAttribute
return null;
}
AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource class AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource子类
protected TransactionAttribute determineTransactionAttribute(AnnotatedElement ae) {
// 获取AnnotatedElement的注解集合,如果有@Transactional,获取到TransactionAttribute返回
if (ae.getAnnotations().length > 0) {
for (TransactionAnnotationParser annotationParser : this.annotationParsers) {
TransactionAttribute attr = annotationParser.parseTransactionAnnotation(ae);
if (attr != null) {
return attr;
}
}
}
return null;
}
SpringTransactionAnnotationParser class 用于解析Transactional annotation
public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement ae) {
// 在AnnotatedElement上的@Transactional获取AnnotationAttributes
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotationAttributes(ae, Transactional.class);
if (attributes != null) {
return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes);
}
return null;
}
以上代码段为判断Advisor是否能应用到目标beanClass的整体逻辑,本质是遍历目标类userServiceImpl的方法,看看方法上是否有@Transactional注解,(这里有个前提: 看看方法上是否有@Transactional注解之前,会先看看这个方法是不是public修饰符的,如果不是,直接遍历下一个方法,表示这个方法不能作为生成代理类的依据,也可以理解为非public的@Transactional方法事务不起作用 ),如果有@Transactional注解,获取其属性值组成的TransactionAttribute,有了TransactionAttribute,就可以说明匹配上了,从而Advisor返回给getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法,从而Advisor返回给(2)处代码并赋值给specificInterceptors,从而可以生成代理类即(3)处代码逻辑。通过这个Advisor会传入生成代理类的方法,代理类的拦截器和切面都是从这个Adviosr拿到的,不用的代理类的Advisor是不同的,spring transaction的Advisor是BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor,见下图;而spring Aspect的Advisor是InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl,详情见 https://yaoyuanyy.github.io/2019/04/28/%E7%BB%86%E8%8A%82%E7%9F%A5%E5%A4%9A%E5%B0%91%20-%20spring%20boot%20aop%E5%8A%A8%E6%80%81%E4%BB%A3%E7%90%86%E8%A7%A3%E6%9E%90%E4%B9%8B%E9%98%B6%E6%AE%B5%E4%BA%8C/[spring boot aop过程解析之阶段二 判断beanName或beanClass是否生成Proxy代理类]
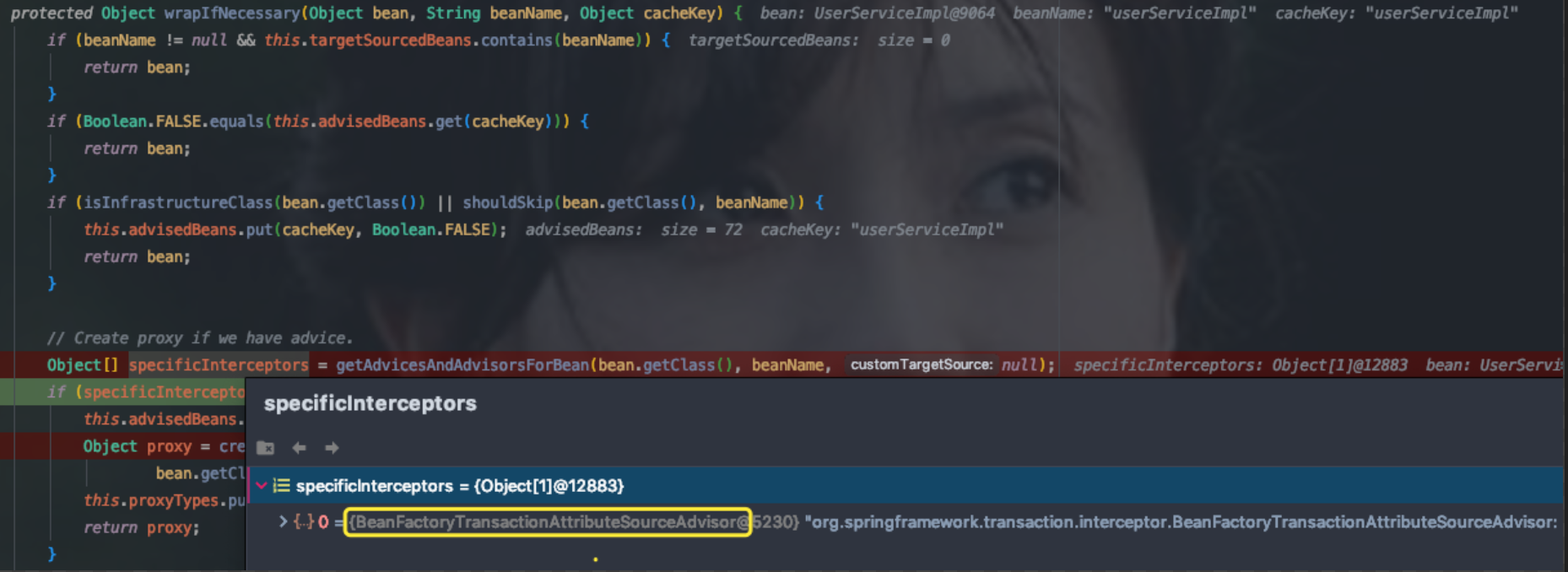
生成代理类
随着Advisor获取到了,开始执行(3)处代码逻辑:生成事务代理类,代码Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)),看其方法逻辑代码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
// this为AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator(proxyTargetClass=true; optimize=false; opaque=false; exposeProxy=false; frozen=false)
// 即proxyFactory的proxyTargetClass和exposeProxy等属性值是从AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator传过来的,
// 而AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreatorproxyTargetClass和exposeProxy等属性值又是通过我们手动声明@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass=?, exposeProxy=?)传进来
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
// 如果proxyFactory.proxyTargetClass为false,但是目标beanClass是类而不是接口,那么需要设置proxyFactory.proxyTargetClass为true,表示使用cglin生成代理
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// 获取advisor,就是上面传过来的BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor实例
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
这个方法生成proxyFactory实例,proxyFactory是管理和配置proxys的工具类,真正负责生成代理类的类是AopProxyFactory,AopProxyFactory.createAopProxy(this)方法生成代理类。this为proxyFactory,从而把proxyFactory中的Advisor、targetClass、proxyTargetClass、exposeProxy一并传到JdkDynamicAopProxy或ObjenesisCglibAopProxy中,由于proxyTargetClass为true且UserServiceImpl不是接口,所以创建了ObjenesisCglibAopProxy实例,即使用cglib生成代理类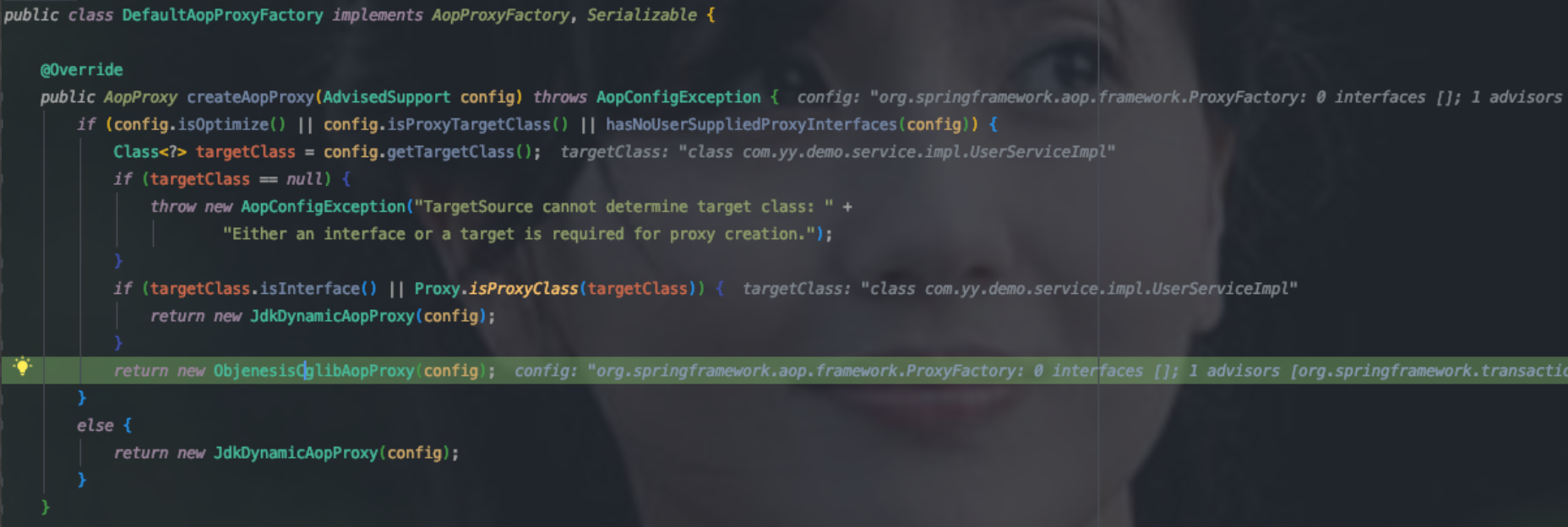
下面是调用cglib的getProxy方法创建代理类,关于这里详见:spring boot aop过程解析之阶段三 CglibAopProxy或JdkDynamicAopProxy生成Proxy代理类阶段。与Aspect生成代理的不同的地方在:此处ProxyFactory中的Advisor是BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor,而Aspect的情况是InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl,所以生成的代理类的拦截器就不同了
spring transaction cglib方式生成代理类的过程中会遍历(遍历的逻辑在Enhancer.emitMethods)目标类的每个方法,使用cglibAopProxy的ProxyCallbackFilter.accept方法判断是否生成代理方法,具体为获取Advisor的Intercepters,获取Intercepters过程中会进行匹配判断,判断逻辑与(2)处相同:调用TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut.matches(method,targetClass)方法判断是否匹配,在详细点说是看看method是否有@Transactional注解和method的修饰符是否为public,两者都满足才生成代理方法,详细逻辑见如下代码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45public int accept(Method method) {
······
Class<?> targetClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
// Proxy is not yet available, but that shouldn't matter.
List<?> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); // 重点代码
boolean haveAdvice = !chain.isEmpty();
boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();
boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();
boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();
if (haveAdvice || !isFrozen) {
if (exposeProxy) {
return AOP_PROXY;
}
String key = method.toString();
// Check to see if we have fixed interceptor to serve this method.
// Else use the AOP_PROXY.
if (isStatic && isFrozen && this.fixedInterceptorMap.containsKey(key)) {
// We know that we are optimizing so we can use the FixedStaticChainInterceptors.
int index = this.fixedInterceptorMap.get(key);
return (index + this.fixedInterceptorOffset);
}
else {
return AOP_PROXY;
}
}
}
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Advised config, Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<Object>(config.getAdvisors().length);
Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass());
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) {
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
// MethodMatcher为TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut
MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, actualClass, hasIntroductions)) {
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
}
return interceptorList;
}
生成的代理类
由于代理类太长,专门放在一个文档中,详见:TODO
我们已经完成了带有@Transactional方法的service类生成代理类的整个过程的解析阐述,可以回答下面的问题了
问题回答
问题:1
2
3
41. service类只要有方法加了@Transactional注解就会生成代理类吗,此处的方法有条件吗
2. spring boot 涉及transaction事务的xxxAutoConfiguration都有哪些
3. spring boot 默认生成代理的方式是cglib还是jdk
4. 什么样的方法可以生成代理方法
回答:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
691. 有的,
生成代理类的条件:必须至少有一个带有@Transactional注解且修饰符是public的方法
生成代理方法的条件:方法必须带有@Transactional注解且修饰符是public的方法
2. spring boot 涉及transaction事务的xxxAutoConfiguration都有哪些
通过spring-boot-autoconfig-xxx.jar的spring.factories文件可知,涉及transaction的AutoConfiguration有
a.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration 用于创建DataSourceTransactionManager实例
b.TransactionAutoConfiguration 用于创建TransactionTemplate实例
c.DataSourceAutoConfiguration 用于创建DataSourceInitializer实例
3. cglib
TransactionAutoConfiguration的内部类上有@ConditionalOnProperty注解,根据这个注解的各属性值配置,决定是加载JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration还是CglibAutoProxyConfiguration,我们知道,’@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)‘会匹配上,所以程序会加载CglibAutoProxyConfiguration类,即spring boot 默认生成事务代理的方式是cglib,具体代码如下
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(TransactionProperties.class)
public class TransactionAutoConfiguration {
······
@Configuration
public static class EnableTransactionManagementConfiguration {
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "false", matchIfMissing = false)
public static class JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
public static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
}
}
4.
a. 非public修饰的方法
不会获取到TransactionInterceptor,但是会在代理类中生成代理方法。只是这个代理方法没有TransactionInterceptor,所以这样的方法事务不会生效
b. private修饰的方法
不会压根不会再代理类中出现,因为Enhancer.generateClass方法中会对目标类的每个方法进行Filter过滤,具体代码如下:
public class VisibilityPredicate implements Predicate {
public boolean evaluate(Object arg) {
Member member = (Member)arg;
int mod = member.getModifiers();
if (Modifier.isPrivate(mod)) {
return false;
} else if (Modifier.isPublic(mod)) {
return true;
} else if (Modifier.isProtected(mod) && this.protectedOk) {
return true;
} else {
return this.samePackageOk && this.pkg.equals(TypeUtils.getPackageName(Type.getType(member.getDeclaringClass())));
}
}
}
public static Collection filter(Collection c, Predicate p) {
Iterator it = c.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
if (!p.evaluate(it.next())) {
it.remove();
}
}
return c;
}
可以看到,当修饰符是private时,evaluate方法返回false,从而触发iterator.remove()方法,从而生成的代理类没有这个方法的代理方法,所以这样的方法事务不会生效
spring transaction 关键词
1 | BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor |
it`s time to sumiray
本文主要阐述了,spring transaction事务生成代理类的过程中,目标类及其方法生成事务代理类和事务代理方法时的条件是什么,认清了什么样的类和方法不能生成事务代理类和事务代理方法,同时讲清了其不能的本质原因。同时,重点列举了与spring transaction有关的AutoConfiguration类有哪些,怎样加载他们。下文,我们阐述下通过curl url访问这些service方法时,spring transaction事务代理类是怎样起做事务提交和回滚作用的


